Abstraction | Encapsulation | Inheritance | Polymorphism | Composition— [Notes]
[Refer LLD Index for all LLD topics]
· Inheritance vs [Aggregation/Composition]
· Aggregation
· Composition
· Abstraction
· Encapsulation
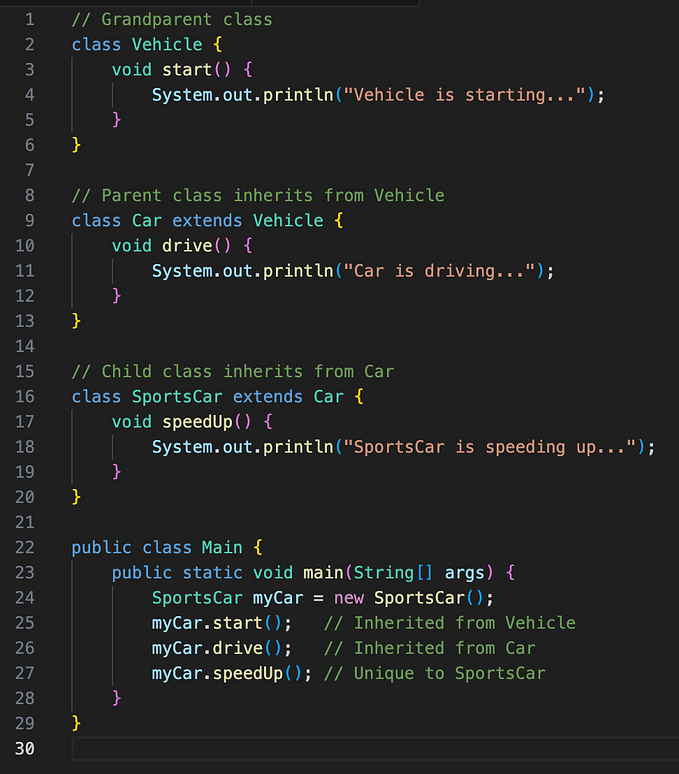
· Inheritance
∘ How is inheritance bad?
· Polymorphism
· Composition
Inheritance vs [Aggregation/Composition]
Extending a class is the first thing that comes to mind when you need to alter an object’s behavior. However, inheritance has several serious caveats that you need to be aware of.
- Inheritance is static. You can’t alter the behavior of an existing object at runtime. You can only replace the whole object with another one that’s created from a different subclass.
- Subclasses can have just one parent class. In most languages, inheritance doesn’t let a class inherit behaviors of multiple classes at the same time.
One of the ways to overcome these caveats is by using Aggregation or Composition instead of Inheritance.
- Both of the alternatives work almost the same way: one object has a reference to another and delegates it some work, whereas with inheritance, the object itself is able to do that work, inheriting the behavior from its superclass.
- With this new approach(Composition/Aggregation) you can easily substitute the linked “helper” object with another, changing the behavior of the container at runtime.
- An object can use the behavior of various classes, having references to multiple objects and delegating them all kinds of work.
Aggregation/composition is the key principle behind many design patterns, including Decorator.
Aggregation
object A contains objects B; B can live without
Composition
object A consists of objects B; A manages life cycle of B; B can’t live without A.
Abstraction
✔ representing an idea/entity that is relevant to a system and hiding everything else.
✔ Hiding the complexity and providing the interface(s)
- 📌 represent all details for an entity in a context
- 📌 omit the non-needed details
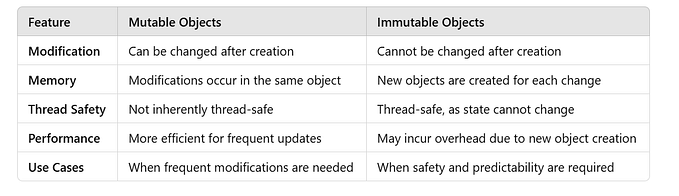
Encapsulation
✔ Holding data and behaviour together
- ➕ Holding data and behaviour together
- ➕ prevents external things from modifying the internal details. [access modifiers]
👍 make everything private | expose as little as possible.
Inheritance
✔ way to organize different entities in the system.

✔Overriding is not the best use of inheritance
📌Use inheritance when talking about physical properties / attributes | Interfaces → Behaviours ➡ when classes have similar physical attribute and one class is extending the arttibute of previous class
- ➕ code reuse
- ➕ extensibility
How is inheritance bad?
- Use inheritance when talking about physical properties / attributes → when classes have similar physical attribute and one class is extending the attribute of previous class
- Interfaces → Behaviours
- Class overload → n behavior will have 2^n types of classes to support all combinations of behavior | solution is to use interfaces
- Code duplication | Solution is to use composition
- Solution → Composition
Favor object composition over class inheritance.
Polymorphism
✔ Many forms
✔ No need to know the real type
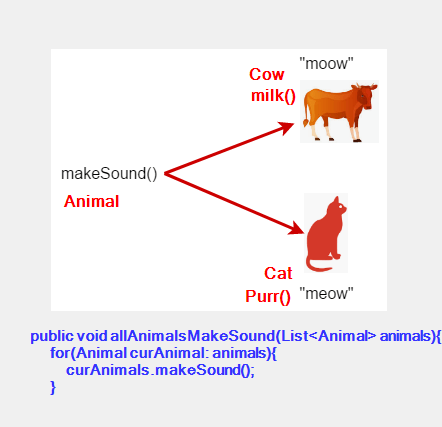
Composition
- Composition prevent code duplication
Favor object composition over class inheritance.
//No composition -> Code duplication
package temp;
public class Animal {
int height;
int weight;
}
public interface Audible {
void makeSound();
}
public interface Walkable {
void walk();
}
public class Dog extends Animal implements Walkable, Audible{
@Override
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("Bow Bow");
}
@Override
public void walk() {
System.out.println("Walk"); //code1 - duplicate code
}
}
public class Cat extends Animal implements Audible {
@Override
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("Meow");
}
}
public class Monkey extends Animal implements Walkable{
@Override
public void walk() {
System.out.println("Walk"); //code2 - duplicate code
}
}//Composition
//Loose coupling
public class Animal {
int height;
int weight;
}
public interface Audible {
void makeSound();
}
public interface Walkable {
void walk();
}
public interface WalkingBehaviour {
void walk();
}
public class SlowWalkingBehaviour implements WalkingBehaviour{
@Override
public void walk() {
System.out.println("Walk");
}
}
public class FastWalkingBehaviour implements WalkingBehaviour{
@Override
public void walk() {
System.out.println("Walk Fast");
}
}
public interface SpeakingBehaviour {
void makeSound();
}
public class Cat extends Animal implements Audible {
SpeakingBehaviour speakingBehaviour;
//Cat has a speaking behaviour --> Composition
public Cat(SpeakingBehaviour speakingBehaviour) {
this.speakingBehaviour = speakingBehaviour;
}
@Override
public void makeSound() {
speakingBehaviour.makeSound();
}
}
public class Dog extends Animal implements Walkable, Audible {
WalkingBehaviour walkingBehaviour;
SpeakingBehaviour speakingBehaviour;
//Dog has a walking + speaking behaviour --> Composition
public Dog(WalkingBehaviour walkingBehaviour, SpeakingBehaviour speakingBehaviour) {
this.speakingBehaviour = speakingBehaviour;
this.walkingBehaviour = walkingBehaviour;
}
@Override
public void makeSound() {
speakingBehaviour.makeSound();
}
@Override
public void walk() {
walkingBehaviour.walk();
}
}
public class Monkey extends Animal implements Walkable {
WalkingBehaviour walkingBehaviour;
//Monkey has a walking behaviour --> Composition
public Monkey(WalkingBehaviour walkingBehaviour) {
this.walkingBehaviour = walkingBehaviour;
}
@Override
public void walk() {
walkingBehaviour.walk();
}
}![Geospatial | GeoHash — [Notes]](https://miro.medium.com/v2/resize:fit:679/0*G2uxyBrzs_Buk6k3.png)
![Union Find | Disjoint Set Union (DSU) — [Notes]](https://miro.medium.com/v2/resize:fit:679/0*HjvG0mec8ReOfyVe.png)
![Two Pointers — [Notes]](https://miro.medium.com/v2/resize:fit:679/0*3s0xJkhsFgQkFvoG.png)